Motivation
Reinforced concrete (RC) structures are an indispensable part of our lives, as our mobility, the industrial performance and the functionality of modern society in general directly depend on the reliability and availability of these structures. Hence, cost-efficient preservation of the integrity of the RC infrastructure over the complete service life is of utmost importance, considering in particular, that modern RC structures have to meet increasing demands with regard to performance. Higher (traffic) loads, longer service life and the use of new materials necessitate a reliable service life prediction method embedded in the framework of a sophisticated management tool.
Project Objectives
The aim of this project is to develop a novel method for the assessment of the safety and durability of RC structures. The method is based on the application of ultrasonic coda wave interferometry (CWI) to RC structures. Laboratory experiments at the specimen scale (nm - cm range) and structure scale (cm - m) provide correlations between specific types of load (i.e. mechanical or thermal) and their effect on the material as well as features of the coda. Numerical modelling using translation, upscaling and localization methods will be applied to distinguish between different types of load. Finally, methods for using the information from the coda will be developed to enable rapid updates of structural models for service life prediction of RC structures.
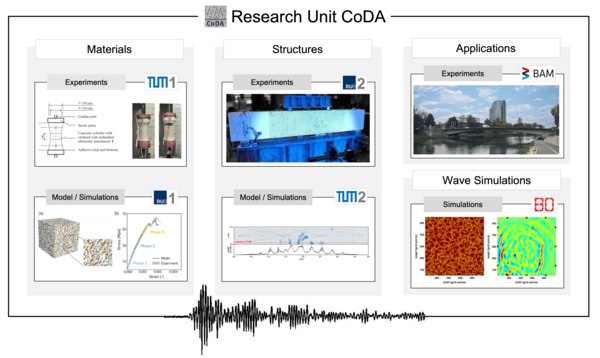
The research units investigations include highly controlled laboratory experiments on influences on the coda signal using smaller scale specimens (TUM1), as well as specimens with structural size (RUB2). Theory and experiment based, a material model is developed (RUB1) and used for silmuation of wave propagation in concrete (BU). Complementary, structural modeling and simulations (TUM2) provide large-scale information. Furthermore, the measurement technology and evaluation methods required for ultrasonic investigations are continuously being enhanced, and the methods are applied to real structures (BAM).
BU : High-Performance Simulations of Wave Propagation for Structure Analysis of Concrete
RUB2 : Thermo-mechanical experiments of RC structures correlated to distributed coda signals
TUM2 : Large scale hybrid models for damage detection in arbitrarily shaped concrete structures